Study description
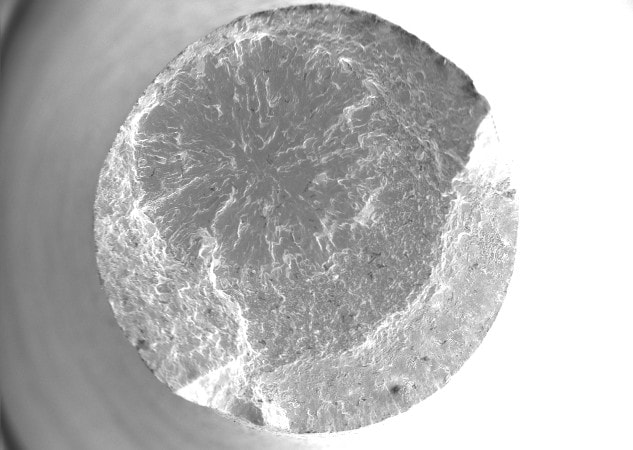
Ti-6Al-4V is the most common used alloy in Additive Manufacturing and predominantly used in aviation and the medical industry. These demanding industries have very high requirements on static mechanical and often fatigue properties. Therefore, the HIP process has become a standard postprocess for eliminating residual porosity in high-performance parts. However, due to lack of standardization and accessible HIP capacity, the common HIP treatment for Additive Manufacturing parts, today, is still derived from temperature-pressure-cycles optimized for casting. To advance the knowledge on HIP treatments for AM parts, while enhancing AM specific material properties, AMPOWER investigates and optimizes HIP cycles for LB-, EB-PBF and BJT in this study.
In the study three HIP cycles with different temperature-pressure-curves are investigated. Low temperature treatments to preserve the specific as build microstructure as well as treatments above the -transus temperature are performed. The resulting material properties of LB-, EB-PBF and BJT specimen are analyzed in 20 different combinations of AM technology and HIP treatment. The study includes a detailed analysis of the density, microstructure and static as well as fatigue strength. AM specific material properties such as anisotropy are investigated.