Watch the video tutorial
Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Potential
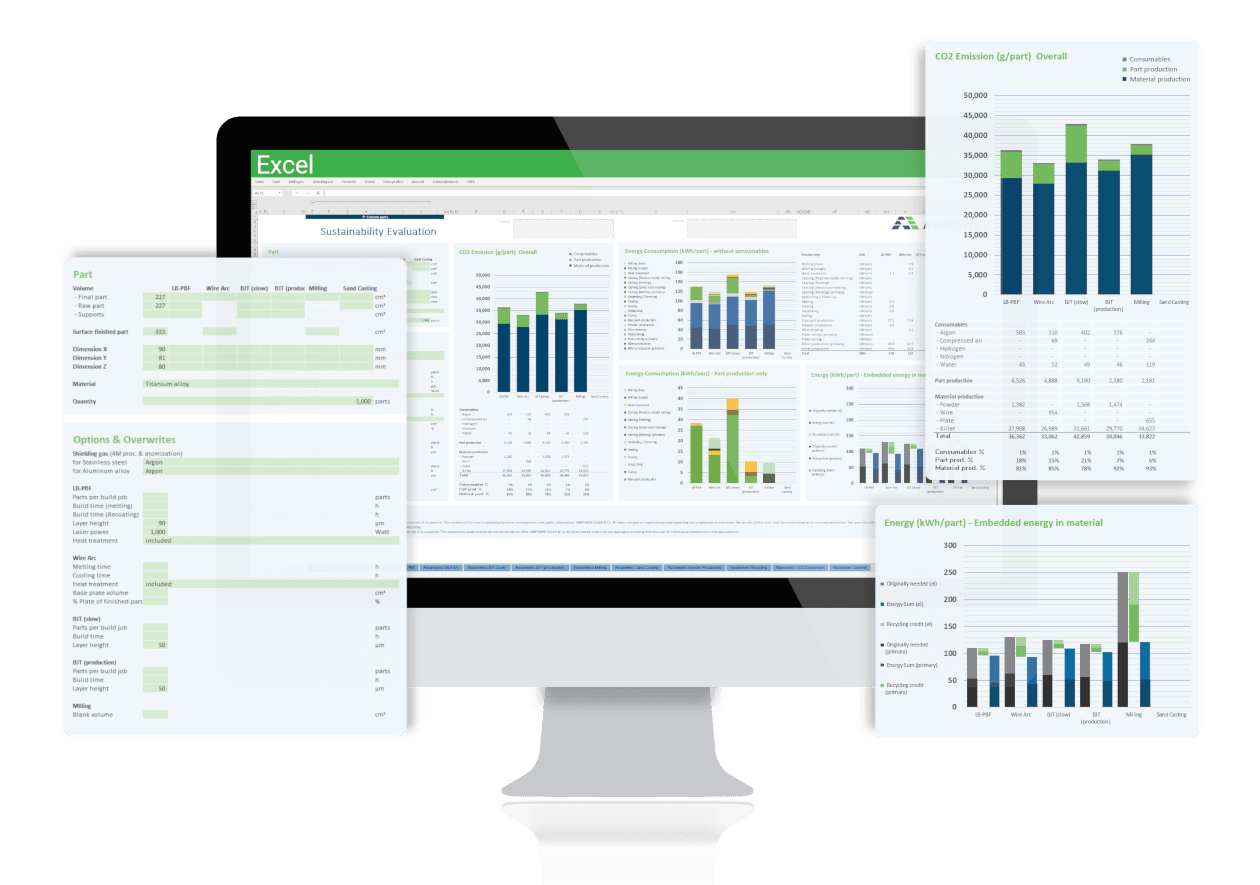
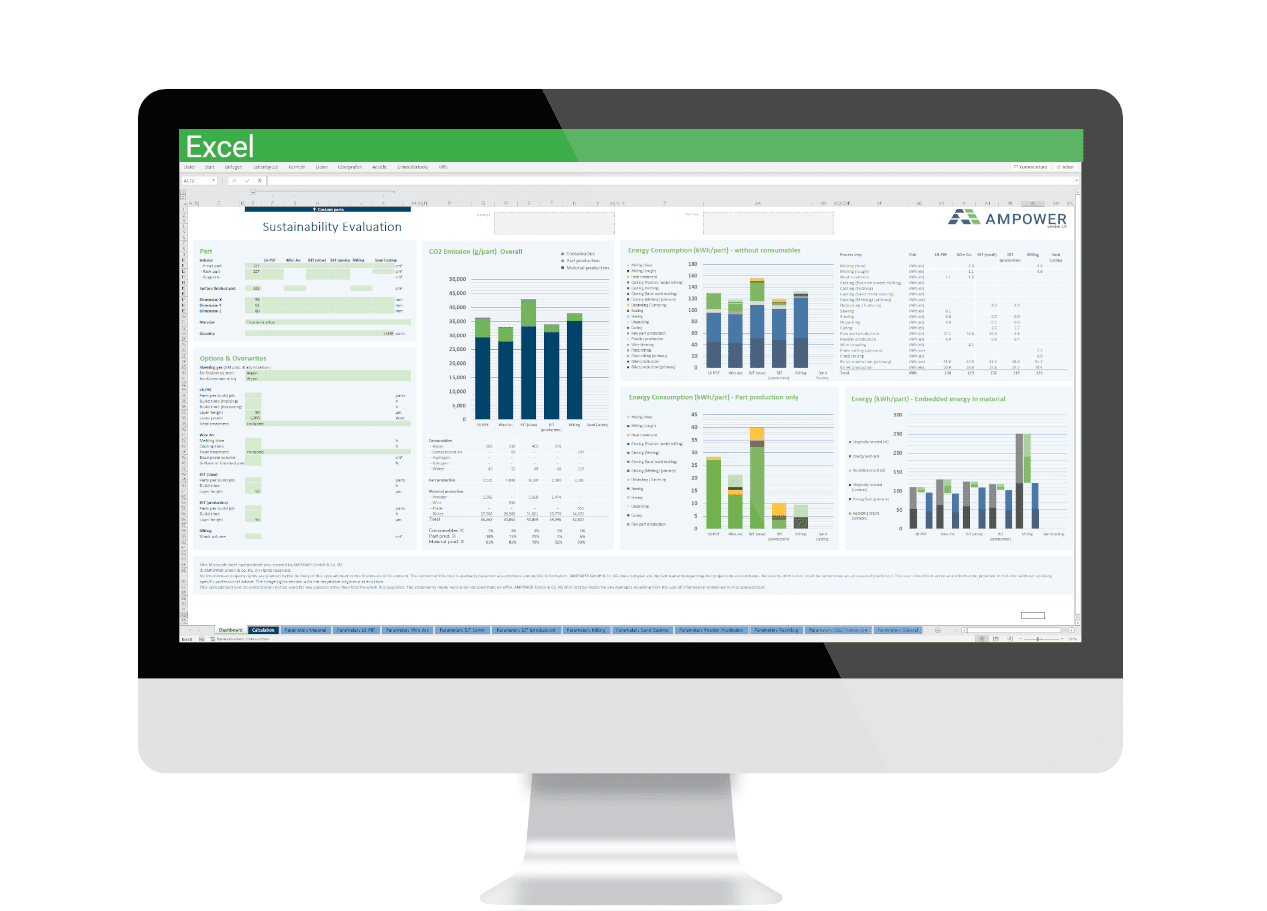
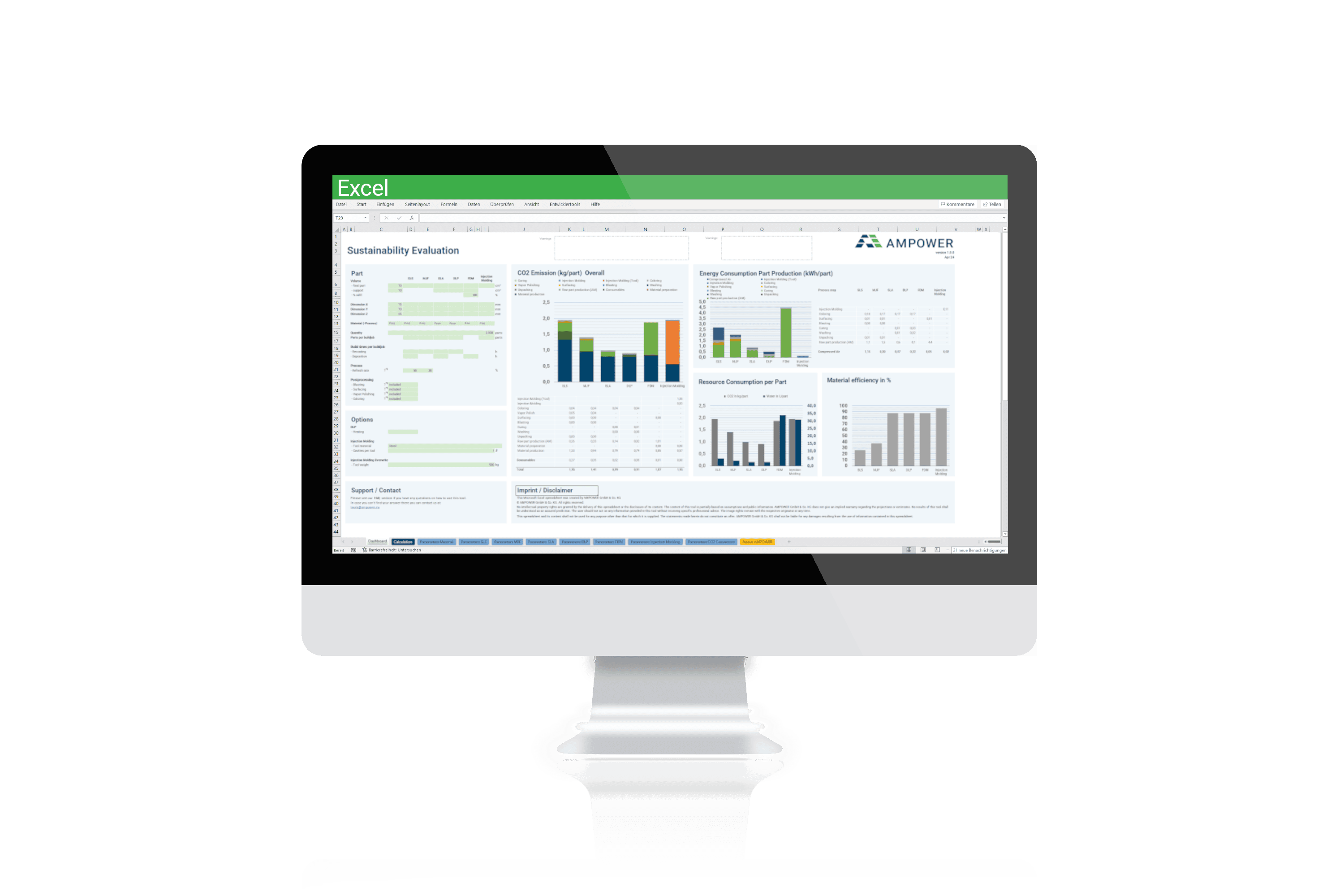
The Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Calculator enables engineers to leverage the potential of a new manufacturing technology. Rising atmospheric CO2 level and resulting weather phenomena have finally changed the general mindset of people, politics and industry regarding fossil fuel emissions over the last 5 years. The majority now strives towards reduced carbon emissions and a more sustainable way of living. The carbon footprint of each product has become an increasing incentive for purchase. Consequently, manufacturers are facing the challenge to reduce or even eliminate the carbon footprint of their products in order to meet today’s and tomorrow’s sustainability requirements. The Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Calculator is a tool designed for manufacturing companies and engineers to calculate the CO2 footprint of their parts.
How does the Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Calculator work?
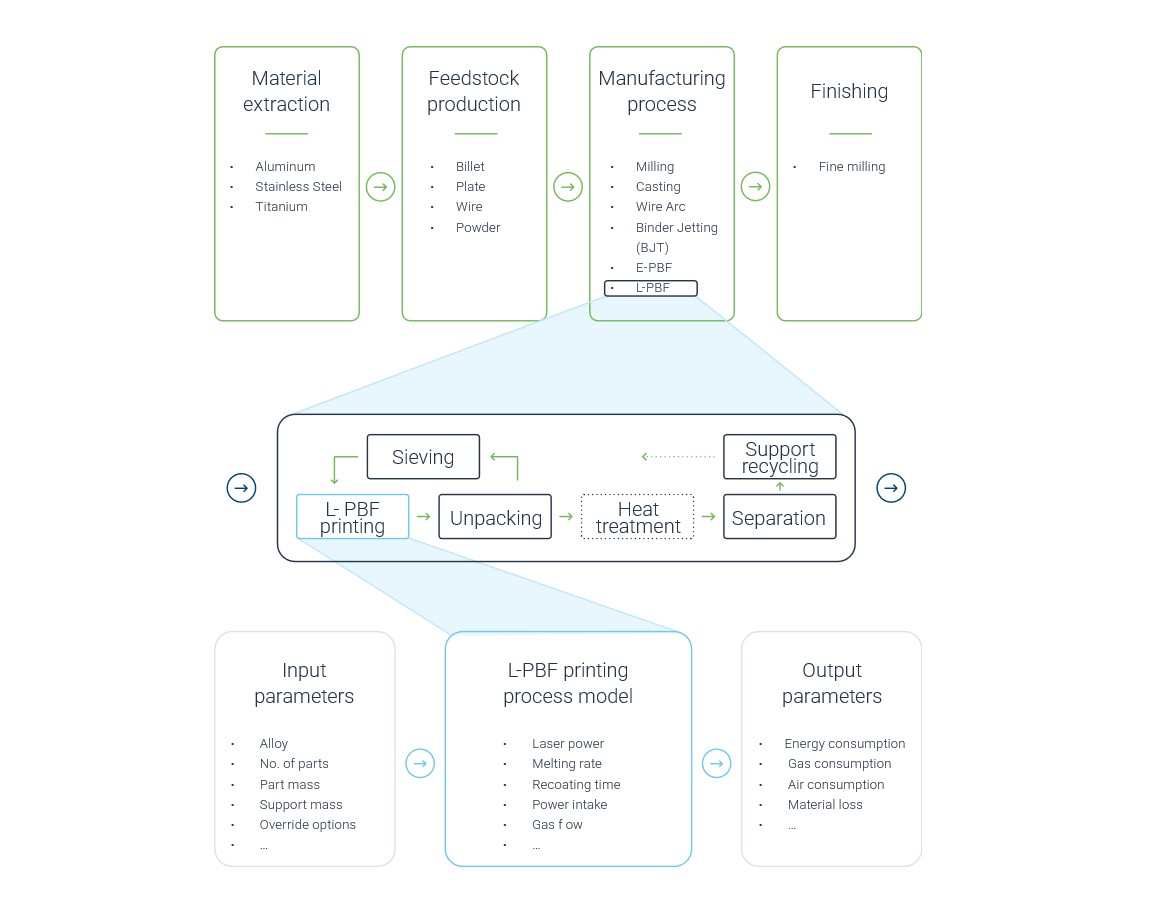
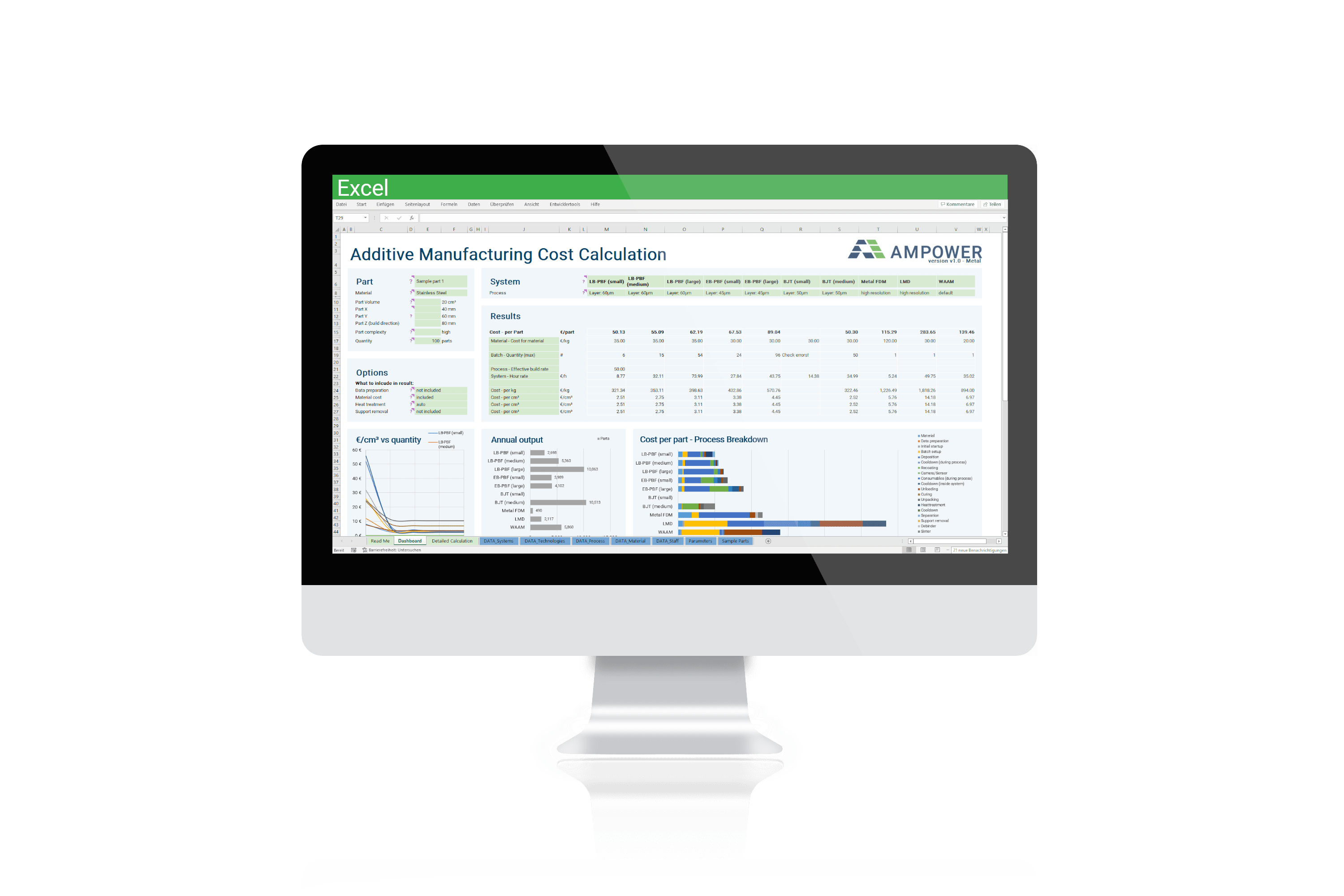
The Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Calculator includes AM as well as conventional metal processing technologies. Each manufacturing process is detailed and broken down to a granular level of its process steps. The description of the different production and manufacturing processes includes all mandatory and optional process steps such as heat treatment for an individualization of the process route. Additionally, material recycling is considered at all sensible stages. The recycling rate can be individually adapted for the feedstock production and within the manufacturing process steps where excess material is produced (e.g. support material or milling chips). For each process step a detailed process model including all input and output parameters is created. Based on this model the Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Calculator calculates consumption of energy and consumables and converts it into CO2 emissions.
Additive Manufacturing can reduce CO2 emissions for Hittech
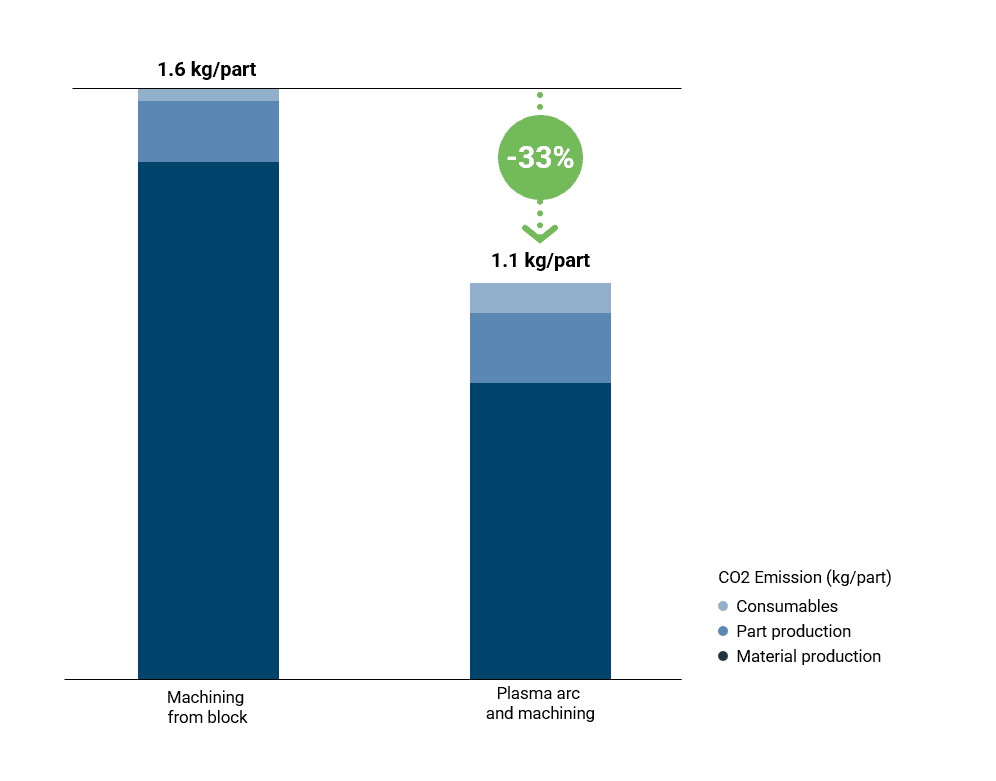
Hittech and Norsk Titanium partnered to manufacture an end part by Plasma Arc Additive Manufacturing, demonstrating how this technology enabled Hittech to achieve over 45% raw material savings. The CO2 analysis conducted by AMPOWER revealed the impact on the CO2 footprint.
Titanium alloys, known for their energy-intensive production processes, make material savings particularly attractive. While part production using Plasma Arc technology consumes slightly more energy than conventional plate manufacturing, the significant material reduction leads to a net positive outcome. AMPOWER’s calculations reveal a 33% reduction in CO2 emissions, accounting for the entire manufacturing process chain, from raw material sourcing to the finished, machined part.
Plasma wire arc included in the calculator
The AMPOWER CO2 Footprint Calculator was used for the analysis of the Hittech application. Besides wire arc and plasma arc technologies, the tool also provides other metal Additive Manufacturing and conventional manufacturing technologies. For this specific use case, the comparison was made with conventional machining.
Loading your part into the Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Calculator
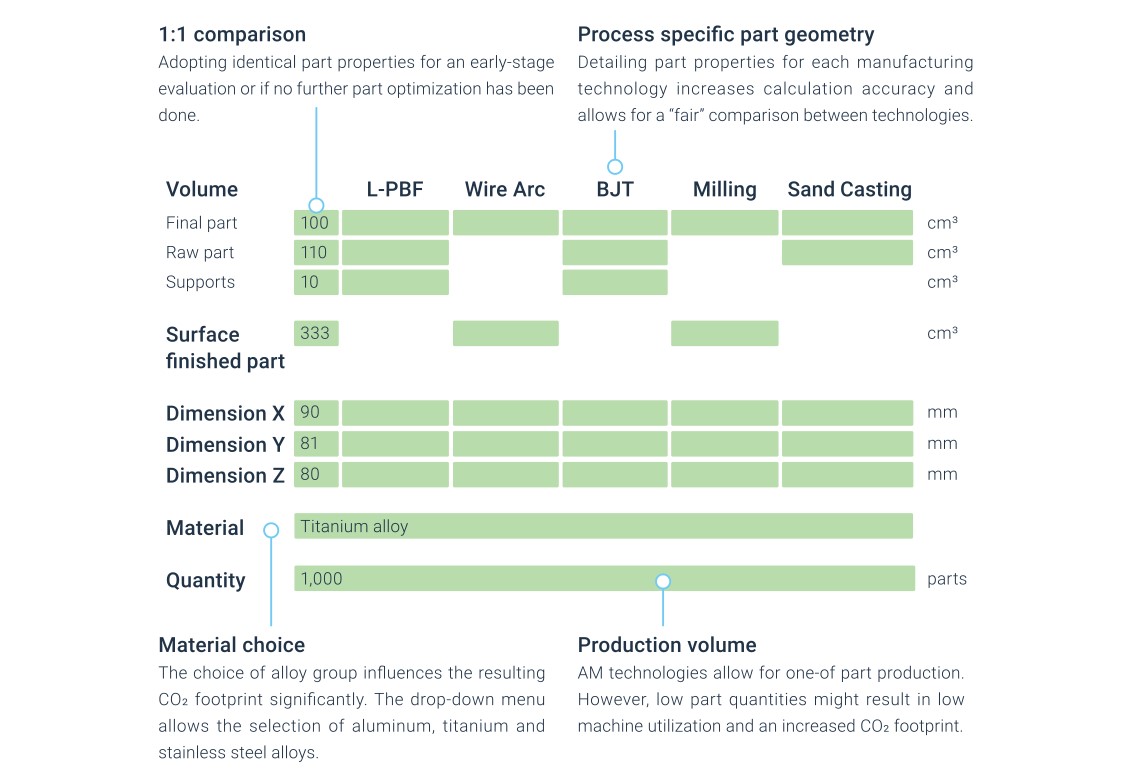
The AMPOWER Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Calculator is calculating the CO2 footprint of a part based on its geometry. Early in the development and design phase many details needed for an extensive Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) are unknown. However, the estimation and comparison of the CO2 footprint of alternative designs and manufacturing technologies will become a valuable decision parameter. AMPOWER’s Sustainability Calculator enables a fast and easy evaluation and comparison. Based on a generic approach, the tool requires minimal input parameters to calculate the CO2 footprint for a multitude of different manufacturing technologies. Additionally, if alternative or optimized part designs were developed, the tool allows a direct comparison of conventional to optimized part designs. This yields the highest result accuracy and a “fair” comparison between different manufacturing technologies.
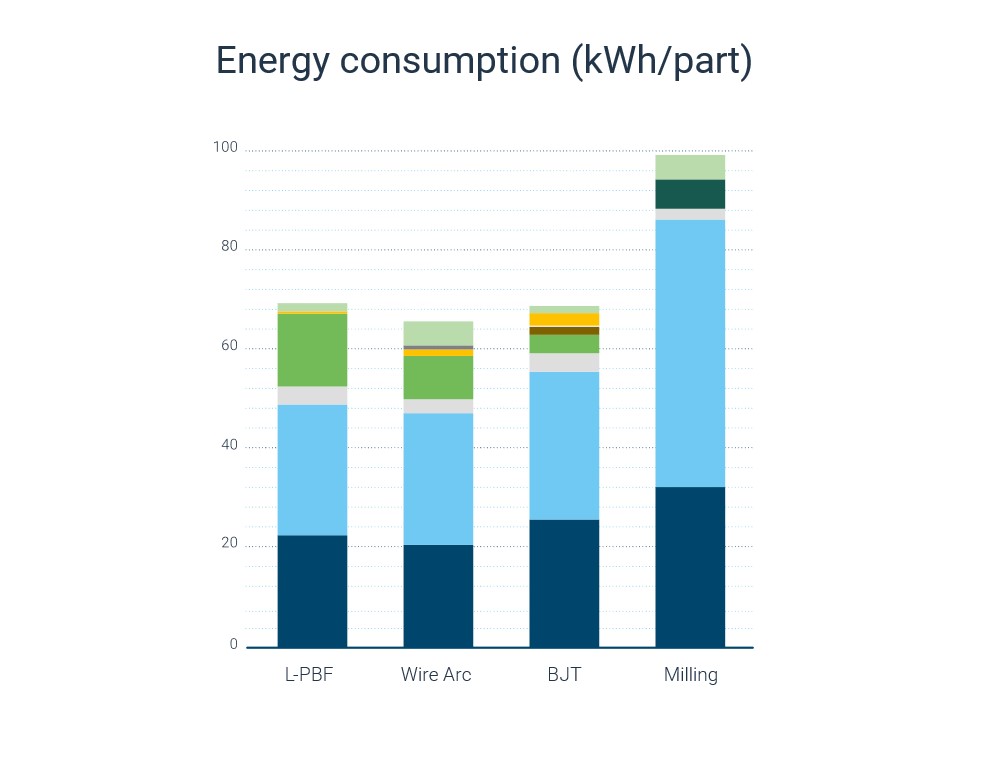
Saving energy means saving CO2
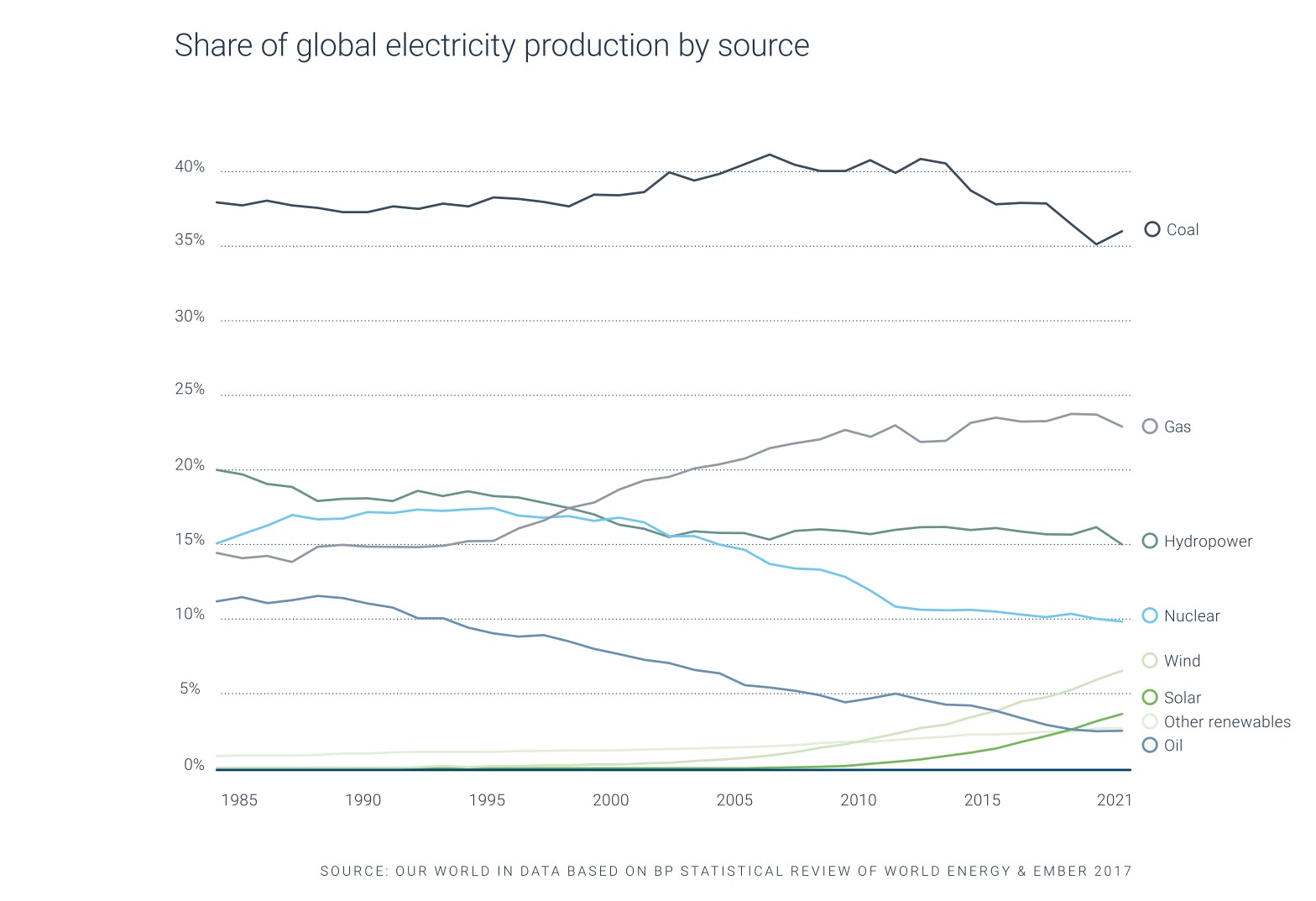
Carbon emissions in manufacturing are directly linked to the energy consumption throughout the process chain. Thus, CO2 emissions can be most effectively reduced by sourcing renewable energy or reducing energy consumption overall. Compared to other industrial processes and manufacturing technologies such as casting, where heat and direct CO2 emission are created by burning fossil fuels, metal Additive Manufacturing is only using electric energy. The required electric energy results in varying amounts of carbon emissions, depending on where it is sourced. Subsequently, manufacturing companies can reduce or eliminate their carbon footprint by sourcing renewable energy. However, calculations show, that the overall increase of global energy consumption makes it nearly impossible to simply switch to renewable energy. Currently carbon emission goals can only be reached, if the overall energy consumption is reduced at the same time. This is why the Additive Manufacturing Sustainability Calculator is mainly based on the energy consumption of each process step.